1.下載 SlackWare 13 的 轉換編譯程式
因為 SwackWare 13 沒有 Dovecot 的安裝套件,所以必須下載原始碼,然後製作成 SwackWare 13 的安裝套件,此套件檔就可以使用 SwackWare 的套件管理程式,來安裝套件。
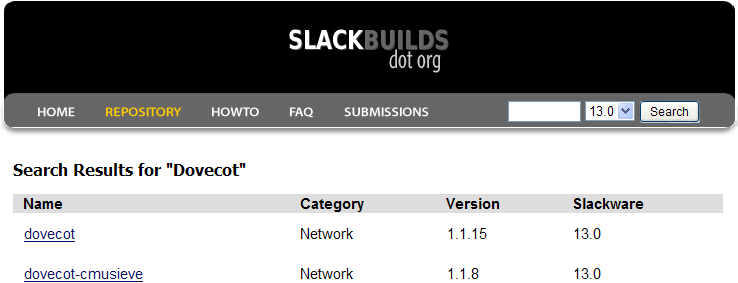
網址 http://www.slackbuilds.org/
右上角的框框輸入Dovecot ,然後SwackWare的版本這裡選擇 13,然後按下 [search]
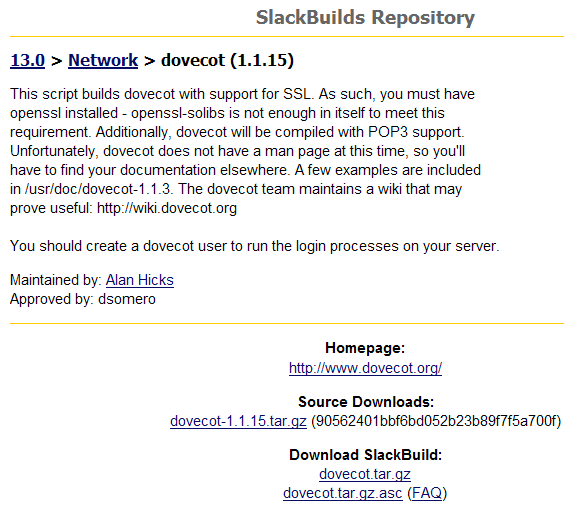
點選 dovecot
下載 dovecot.tar.gz 及 dovecot-1.1.15.tar.gz(此檔也可以到官方網站下載,但版本要和這邊的一樣),將檔案存放在 /tmp 資料夾內
先建立 dovecot 相關的帳號以及相關權限
# groupadd -g 202 dovecot # useradd -d /dev/null -s /bin/false -u 202 -g 202 dovecot # mkdir /var/run/dovecot(建立 dovecot 執行時,相關資料暫存的資料夾)# mkdir /var/mail_empty(參考設定檔dovecot.conf 的 mail_location 說明)
編譯及產生 SlackWare 專用的安裝套件
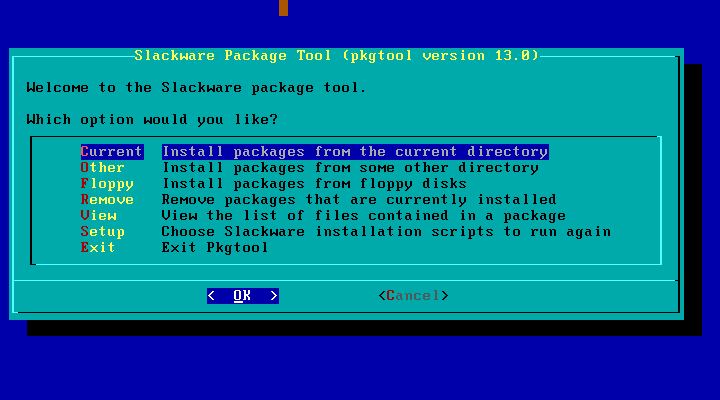
# cd /tmp # tar -zxvf dovecot.tar.gz # mv dovecot-1.1.15.tar.gz dovecot # cd /tmp/dovecot # ./dovecot.SlackBuild接下來就開始進行編譯,然後包裝成 SlackWare 專用的安裝套件當出現Slackware package /tmp/dovecot-1.1.15-i486-1_SBo.tgz created.表示已產生 SwackWare 的專用安裝套件# cd /tmp # pkgtool
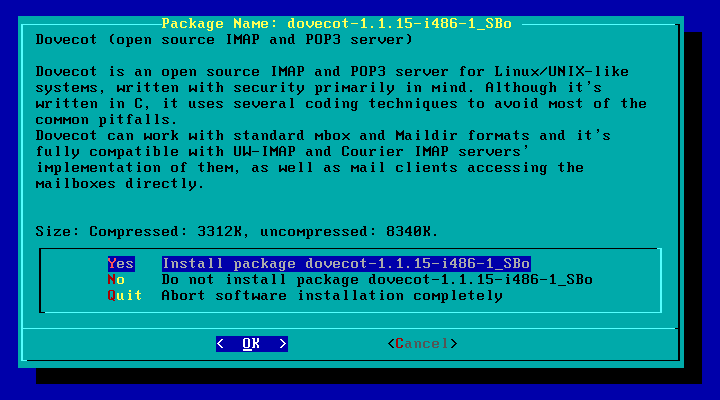
選擇 Current , 按下 Enter
選擇 Yes 就可以安裝套件了。
編輯設定檔 dovecot.conf
# cp /etc/dovecot-example.conf /etc/dovecot.conf # vi dovecot.conf## Dovecot configuration file # If you're in a hurry, see http://wiki.dovecot.org/QuickConfiguration # "dovecot -n" command gives a clean output of the changed settings. Use it # instead of copy&pasting this file when posting to the Dovecot mailing list. # '#' character and everything after it is treated as comments. Extra spaces # and tabs are ignored. If you want to use either of these explicitly, put the # value inside quotes, eg.: key = "# char and trailing whitespace " # Default values are shown for each setting, it's not required to uncomment # those. These are exceptions to this though: No sections (e.g. namespace {}) # or plugin settings are added by default, they're listed only as examples. # Paths are also just examples with the real defaults being based on configure # options. The paths listed here are for configure --prefix=/usr # --sysconfdir=/etc --localstatedir=/var --with-ssldir=/etc/ssl # Base directory where to store runtime data. #base_dir = /var/run/dovecot/ base_dir = /var/run/dovecot/=>加入# Protocols we want to be serving: imap imaps pop3 pop3s # If you only want to use dovecot-auth, you can set this to "none". #protocols = imap imaps protocols = pop3=>加入# A space separated list of IP or host addresses where to listen in for # connections. "*" listens in all IPv4 interfaces. "[::]" listens in all IPv6 # interfaces. Use "*, [::]" for listening both IPv4 and IPv6. # # If you want to specify ports for each service, you will need to configure # these settings inside the protocol imap/pop3 { ... } section, so you can # specify different ports for IMAP/POP3. For example: # protocol imap { # listen = *:10143 # ssl_listen = *:10943 # .. # } # protocol pop3 { # listen = *:10100 # .. # } #listen = * # Disable LOGIN command and all other plaintext authentications unless # SSL/TLS is used (LOGINDISABLED capability). Note that if the remote IP # matches the local IP (ie. you're connecting from the same computer), the # connection is considered secure and plaintext authentication is allowed. #disable_plaintext_auth = yes disable_plaintext_auth = no=>加入# Should all IMAP and POP3 processes be killed when Dovecot master process # shuts down. Setting this to "no" means that Dovecot can be upgraded without # forcing existing client connections to close (although that could also be # a problem if the upgrade is eg. because of a security fix). This however # means that after master process has died, the client processes can't write # to log files anymore. #shutdown_clients = yes ## ## Logging ## # Log file to use for error messages, instead of sending them to syslog. # /dev/stderr can be used to log into stderr. #log_path = log_path =/var/log/pop3=>加入# Log file to use for informational and debug messages. # Default is the same as log_path. #info_log_path = info_log_path =/var/log/pop3=>加入# Prefix for each line written to log file. % codes are in strftime(3) # format. #log_timestamp = "%b %d %H:%M:%S " log_timestamp = "%b %d %H:%M:%S "=>加入# Syslog facility to use if you're logging to syslog. Usually if you don't # want to use "mail", you'll use local0..local7. Also other standard # facilities are supported. #syslog_facility = mail ## ## SSL settings ## # IP or host address where to listen in for SSL connections. Remember to also # add imaps and/or pop3s to protocols setting. Defaults to same as "listen" # setting if not specified. #ssl_listen = # Disable SSL/TLS support. <doc/wiki/SSL.txt> #ssl_disable = no ssl_disable = yes=>加入# PEM encoded X.509 SSL/TLS certificate and private key. They're opened before # dropping root privileges, so keep the key file unreadable by anyone but # root. Included doc/mkcert.sh can be used to easily generate self-signed # certificate, just make sure to update the domains in dovecot-openssl.cnf #ssl_cert_file = /etc/ssl/certs/dovecot.pem #ssl_key_file = /etc/ssl/private/dovecot.pem # If key file is password protected, give the password here. Alternatively # give it when starting dovecot with -p parameter. Since this file is often # world-readable, you may want to place this setting instead to a different # root owned 0600 file by using !include_try <path>. #ssl_key_password = # File containing trusted SSL certificate authorities. Set this only if you # intend to use ssl_verify_client_cert=yes. The CAfile should contain the # CA-certificate(s) followed by the matching CRL(s). #ssl_ca_file = # Request client to send a certificate. If you also want to require it, set # ssl_require_client_cert=yes in auth section. #ssl_verify_client_cert = no # Which field from certificate to use for username. commonName and # x500UniqueIdentifier are the usual choices. You'll also need to set # ssl_username_from_cert=yes. #ssl_cert_username_field = commonName # How often to regenerate the SSL parameters file. Generation is quite CPU # intensive operation. The value is in hours, 0 disables regeneration # entirely. #ssl_parameters_regenerate = 168 # SSL ciphers to use #ssl_cipher_list = ALL:!LOW:!SSLv2 # Show protocol level SSL errors. #verbose_ssl = no ## ## Login processes ## # <doc/wiki/LoginProcess.txt> # Directory where authentication process places authentication UNIX sockets # which login needs to be able to connect to. The sockets are created when # running as root, so you don't have to worry about permissions. Note that # everything in this directory is deleted when Dovecot is started. #login_dir = /var/run/dovecot/login login_dir = /var/run/dovecot/login=>加入# chroot login process to the login_dir. Only reason not to do this is if you # wish to run the whole Dovecot without roots. <doc/wiki/Rootless.txt> #login_chroot = yes # User to use for the login process. Create a completely new user for this, # and don't use it anywhere else. The user must also belong to a group where # only it has access, it's used to control access for authentication process. # Note that this user is NOT used to access mails. <doc/wiki/UserIds.txt> #login_user = dovecot # Set max. process size in megabytes. If you don't use # login_process_per_connection you might need to grow this. #login_process_size = 64 # Should each login be processed in it's own process (yes), or should one # login process be allowed to process multiple connections (no)? Yes is more # secure, espcially with SSL/TLS enabled. No is faster since there's no need # to create processes all the time. #login_process_per_connection = yes # Number of login processes to keep for listening new connections. #login_processes_count = 3 # Maximum number of login processes to create. The listening process count # usually stays at login_processes_count, but when multiple users start logging # in at the same time more extra processes are created. To prevent fork-bombing # we check only once in a second if new processes should be created - if all # of them are used at the time, we double their amount until the limit set by # this setting is reached. #login_max_processes_count = 128 # Maximum number of connections allowed per each login process. This setting # is used only if login_process_per_connection=no. Once the limit is reached, # the process notifies master so that it can create a new login process. #login_max_connections = 256 # Greeting message for clients. #login_greeting = Dovecot ready. # Space-separated list of elements we want to log. The elements which have # a non-empty variable value are joined together to form a comma-separated # string. #login_log_format_elements = user=<%u> method=%m rip=%r lip=%l %c # Login log format. %$ contains login_log_format_elements string, %s contains # the data we want to log. #login_log_format = %$: %s ## ## Mailbox locations and namespaces ## # Location for users' mailboxes. This is the same as the old default_mail_env # setting. The default is empty, which means that Dovecot tries to find the # mailboxes automatically. This won't work if the user doesn't have any mail # yet, so you should explicitly tell Dovecot the full location. # # If you're using mbox, giving a path to the INBOX file (eg. /var/mail/%u) # isn't enough. You'll also need to tell Dovecot where the other mailboxes are # kept. This is called the "root mail directory", and it must be the first # path given in the mail_location setting. # # There are a few special variables you can use, eg.: # # %u - username # %n - user part in user@domain, same as %u if there's no domain # %d - domain part in user@domain, empty if there's no domain # %h - home directory # # See <doc/wiki/Variables.txt> for full list. Some examples: # # mail_location = maildir:~/Maildir # mail_location = mbox:~/mail:INBOX=/var/mail/%u # mail_location = mbox:/var/mail/%d/%1n/%n:INDEX=/var/indexes/%d/%1n/%n # # <doc/wiki/MailLocation.txt> # #mail_location = mail_location = mbox:/var/mail_empty:INBOX=/var/mail/%u:INDEX=MEMORY=>加入 (當使用者收信時,直接從 SendMail 的收信檔 [/var/mail/%u] 直接下載信件, 下載信件時,不會在,使用者的家目錄,建立一個mail的資料夾 但是,必須建立一個 mail_empty 唯讀-資料夾 # mkdir /var/mail_empty mail_location = mbox:~/mail:INBOX=/var/mail/%u (使用者收信時,直接從 SendMail 的收信檔 [/var/mail/%u] 直接下載信件, 但是,會在使用者的家目錄建立一個mail的資料夾) 資料參考:http://wiki.dovecot.org/MailLocation/Mbox 內的[Only /var/mail/ mboxes]說明# If you need to set multiple mailbox locations or want to change default # namespace settings, you can do it by defining namespace sections. # # You can have private, shared and public namespaces. The only difference # between them is how Dovecot announces them to client via NAMESPACE # extension. Shared namespaces are meant for user-owned mailboxes which are # shared to other users, while public namespaces are for more globally # accessible mailboxes. # # REMEMBER: If you add any namespaces, the default namespace must be added # explicitly, ie. mail_location does nothing unless you have a namespace # without a location setting. Default namespace is simply done by having a # namespace with empty prefix. #namespace private { # Hierarchy separator to use. You should use the same separator for all # namespaces or some clients get confused. '/' is usually a good one. # The default however depends on the underlying mail storage format. #separator = # Prefix required to access this namespace. This needs to be different for # all namespaces. For example "Public/". #prefix = # Physical location of the mailbox. This is in same format as # mail_location, which is also the default for it. #location = # There can be only one INBOX, and this setting defines which namespace # has it. #inbox = no # If namespace is hidden, it's not advertised to clients via NAMESPACE # extension. You'll most likely also want to set list=no. This is mostly # useful when converting from another server with different namespaces which # you want to deprecate but still keep working. For example you can create # hidden namespaces with prefixes "~/mail/", "~%u/mail/" and "mail/". #hidden = yes # Show the mailboxes under this namespace with LIST command. This makes the # namespace visible for clients that don't support NAMESPACE extension. #list = yes # Namespace handles its own subscriptions. If set to "no", the parent # namespace handles them (empty prefix should always have this as "yes") #subscriptions = yes #} # System user and group used to access mails. If you use multiple, userdb # can override these by returning uid or gid fields. You can use either numbers # or names. <doc/wiki/UserIds.txt> #mail_uid = #mail_gid = # Group to enable temporarily for privileged operations. Currently this is # used only with INBOX when either its initial creation or dotlocking fails. # Typically this is set to "mail" to give access to /var/mail. #mail_privileged_group = # Grant access to these supplementary groups for mail processes. Typically # these are used to set up access to shared mailboxes. Note that it may be # dangerous to set these if users can create symlinks (e.g. if "mail" group is # set here, ln -s /var/mail ~/mail/var could allow a user to delete others' # mailboxes, or ln -s /secret/shared/box ~/mail/mybox would allow reading it). #mail_access_groups = # Allow full filesystem access to clients. There's no access checks other than # what the operating system does for the active UID/GID. It works with both # maildir and mboxes, allowing you to prefix mailboxes names with eg. /path/ # or ~user/. #mail_full_filesystem_access = no ## ## Mail processes ## # Enable mail process debugging. This can help you figure out why Dovecot # isn't finding your mails. #mail_debug = no mail_debug = yes=>加入# Log prefix for mail processes. See <doc/wiki/Variables.txt> for list of # possible variables you can use. #mail_log_prefix = "%Us(%u): " # Max. number of lines a mail process is allowed to log per second before it's # throttled. 0 means unlimited. Typically there's no need to change this # unless you're using mail_log plugin, which may log a lot. This setting is # ignored while mail_debug=yes to avoid pointless throttling. #mail_log_max_lines_per_sec = 10 # Don't use mmap() at all. This is required if you store indexes to shared # filesystems (NFS or clustered filesystem). #mmap_disable = no # Rely on O_EXCL to work when creating dotlock files. NFS supports O_EXCL # since version 3, so this should be safe to use nowadays by default. #dotlock_use_excl = yes # Don't use fsync() or fdatasync() calls. This makes the performance better # at the cost of potential data loss if the server (or the file server) # goes down. #fsync_disable = no # Mail storage exists in NFS. Set this to yes to make Dovecot flush NFS caches # whenever needed. If you're using only a single mail server this isn't needed. #mail_nfs_storage = no # Mail index files also exist in NFS. Setting this to yes requires # mmap_disable=yes and fsync_disable=no. #mail_nfs_index = no # Locking method for index files. Alternatives are fcntl, flock and dotlock. # Dotlocking uses some tricks which may create more disk I/O than other locking # methods. NFS users: flock doesn't work, remember to change mmap_disable. #lock_method = fcntl # Drop all privileges before exec()ing the mail process. This is mostly # meant for debugging, otherwise you don't get core dumps. It could be a small # security risk if you use single UID for multiple users, as the users could # ptrace() each others processes then. #mail_drop_priv_before_exec = no # Show more verbose process titles (in ps). Currently shows user name and # IP address. Useful for seeing who are actually using the IMAP processes # (eg. shared mailboxes or if same uid is used for multiple accounts). #verbose_proctitle = no # Valid UID range for users, defaults to 500 and above. This is mostly # to make sure that users can't log in as daemons or other system users. # Note that denying root logins is hardcoded to dovecot binary and can't # be done even if first_valid_uid is set to 0. #first_valid_uid = 500 #last_valid_uid = 0 # Valid GID range for users, defaults to non-root/wheel. Users having # non-valid GID as primary group ID aren't allowed to log in. If user # belongs to supplementary groups with non-valid GIDs, those groups are # not set. #first_valid_gid = 1 #last_valid_gid = 0 # Maximum number of running mail processes. When this limit is reached, # new users aren't allowed to log in. #max_mail_processes = 512 # Set max. process size in megabytes. Most of the memory goes to mmap()ing # files, so it shouldn't harm much even if this limit is set pretty high. #mail_process_size = 256 # Maximum allowed length for mail keyword name. It's only forced when trying # to create new keywords. #mail_max_keyword_length = 50 # ':' separated list of directories under which chrooting is allowed for mail # processes (ie. /var/mail will allow chrooting to /var/mail/foo/bar too). # This setting doesn't affect login_chroot, mail_chroot or auth chroot # settings. If this setting is empty, "/./" in home dirs are ignored. # WARNING: Never add directories here which local users can modify, that # may lead to root exploit. Usually this should be done only if you don't # allow shell access for users. <doc/wiki/Chrooting.txt> #valid_chroot_dirs = # Default chroot directory for mail processes. This can be overridden for # specific users in user database by giving /./ in user's home directory # (eg. /home/./user chroots into /home). Note that usually there is no real # need to do chrooting, Dovecot doesn't allow users to access files outside # their mail directory anyway. If your home directories are prefixed with # the chroot directory, append "/." to mail_chroot. <doc/wiki/Chrooting.txt> #mail_chroot = ## ## Mailbox handling optimizations ## # The minimum number of mails in a mailbox before updates are done to cache # file. This allows optimizing Dovecot's behavior to do less disk writes at # the cost of more disk reads. #mail_cache_min_mail_count = 0 # When IDLE command is running, mailbox is checked once in a while to see if # there are any new mails or other changes. This setting defines the minimum # time in seconds to wait between those checks. Dovecot can also use dnotify, # inotify and kqueue to find out immediately when changes occur. #mailbox_idle_check_interval = 30 # Save mails with CR+LF instead of plain LF. This makes sending those mails # take less CPU, especially with sendfile() syscall with Linux and FreeBSD. # But it also creates a bit more disk I/O which may just make it slower. # Also note that if other software reads the mboxes/maildirs, they may handle # the extra CRs wrong and cause problems. #mail_save_crlf = no ## ## Maildir-specific settings ## # By default LIST command returns all entries in maildir beginning with a dot. # Enabling this option makes Dovecot return only entries which are directories. # This is done by stat()ing each entry, so it causes more disk I/O. # (For systems setting struct dirent->d_type, this check is free and it's # done always regardless of this setting) #maildir_stat_dirs = no # When copying a message, do it with hard links whenever possible. This makes # the performance much better, and it's unlikely to have any side effects. #maildir_copy_with_hardlinks = yes # When copying a message, try to preserve the base filename. Only if the # destination mailbox already contains the same name (ie. the mail is being # copied there twice), a new name is given. The destination filename check is # done only by looking at dovecot-uidlist file, so if something outside # Dovecot does similar filename preserving copies, you may run into problems. # NOTE: This setting requires maildir_copy_with_hardlinks = yes to work. #maildir_copy_preserve_filename = no ## ## mbox-specific settings ## # Which locking methods to use for locking mbox. There are four available: # dotlock: Create <mailbox>.lock file. This is the oldest and most NFS-safe # solution. If you want to use /var/mail/ like directory, the users # will need write access to that directory. # dotlock_try: Same as dotlock, but if it fails because of permissions or # because there isn't enough disk space, just skip it. # fcntl : Use this if possible. Works with NFS too if lockd is used. # flock : May not exist in all systems. Doesn't work with NFS. # lockf : May not exist in all systems. Doesn't work with NFS. # # You can use multiple locking methods; if you do the order they're declared # in is important to avoid deadlocks if other MTAs/MUAs are using multiple # locking methods as well. Some operating systems don't allow using some of # them simultaneously. #mbox_read_locks = fcntl #mbox_write_locks = dotlock fcntl # Maximum time in seconds to wait for lock (all of them) before aborting. #mbox_lock_timeout = 300 # If dotlock exists but the mailbox isn't modified in any way, override the # lock file after this many seconds. #mbox_dotlock_change_timeout = 120 # When mbox changes unexpectedly we have to fully read it to find out what # changed. If the mbox is large this can take a long time. Since the change # is usually just a newly appended mail, it'd be faster to simply read the # new mails. If this setting is enabled, Dovecot does this but still safely # fallbacks to re-reading the whole mbox file whenever something in mbox isn't # how it's expected to be. The only real downside to this setting is that if # some other MUA changes message flags, Dovecot doesn't notice it immediately. # Note that a full sync is done with SELECT, EXAMINE, EXPUNGE and CHECK # commands. #mbox_dirty_syncs = yes # Like mbox_dirty_syncs, but don't do full syncs even with SELECT, EXAMINE, # EXPUNGE or CHECK commands. If this is set, mbox_dirty_syncs is ignored. #mbox_very_dirty_syncs = no # Delay writing mbox headers until doing a full write sync (EXPUNGE and CHECK # commands and when closing the mailbox). This is especially useful for POP3 # where clients often delete all mails. The downside is that our changes # aren't immediately visible to other MUAs. #mbox_lazy_writes = yes # If mbox size is smaller than this (in kilobytes), don't write index files. # If an index file already exists it's still read, just not updated. #mbox_min_index_size = 0 ## ## dbox-specific settings ## # Maximum dbox file size in kilobytes until it's rotated. #dbox_rotate_size = 2048 # Minimum dbox file size in kilobytes before it's rotated # (overrides dbox_rotate_days) #dbox_rotate_min_size = 16 # Maximum dbox file age in days until it's rotated. Day always begins from # midnight, so 1 = today, 2 = yesterday, etc. 0 = check disabled. #dbox_rotate_days = 0 ## ## IMAP specific settings ## protocol imap { # Login executable location. #login_executable = /usr/libexec/dovecot/imap-login # IMAP executable location. Changing this allows you to execute other # binaries before the imap process is executed. # # This would write rawlogs into ~/dovecot.rawlog/ directory: # mail_executable = /usr/libexec/dovecot/rawlog /usr/libexec/dovecot/imap # # This would attach gdb into the imap process and write backtraces into # /tmp/gdbhelper.* files: # mail_executable = /usr/libexec/dovecot/gdbhelper /usr/libexec/dovecot/imap # #mail_executable = /usr/libexec/dovecot/imap # Maximum IMAP command line length in bytes. Some clients generate very long # command lines with huge mailboxes, so you may need to raise this if you get # "Too long argument" or "IMAP command line too large" errors often. #imap_max_line_length = 65536 # Maximum number of IMAP connections allowed for a user from each IP address. # NOTE: The username is compared case-sensitively. #mail_max_userip_connections = 10 # Support for dynamically loadable plugins. mail_plugins is a space separated # list of plugins to load. #mail_plugins = #mail_plugin_dir = /usr/lib/dovecot/imap # Send IMAP capabilities in greeting message. This makes it unnecessary for # clients to request it with CAPABILITY command, so it saves one round-trip. # Many clients however don't understand it and ask the CAPABILITY anyway. #login_greeting_capability = no # IMAP logout format string: # %i - total number of bytes read from client # %o - total number of bytes sent to client #imap_logout_format = bytes=%i/%o # Override the IMAP CAPABILITY response. #imap_capability = # Workarounds for various client bugs: # delay-newmail: # Send EXISTS/RECENT new mail notifications only when replying to NOOP # and CHECK commands. Some clients ignore them otherwise, for example OSX # Mail (<v2.1). Outlook Express breaks more badly though, without this it # may show user "Message no longer in server" errors. Note that OE6 still # breaks even with this workaround if synchronization is set to # "Headers Only". # netscape-eoh: # Netscape 4.x breaks if message headers don't end with the empty "end of # headers" line. Normally all messages have this, but setting this # workaround makes sure that Netscape never breaks by adding the line if # it doesn't exist. This is done only for FETCH BODY[HEADER.FIELDS..] # commands. Note that RFC says this shouldn't be done. # tb-extra-mailbox-sep: # With mbox storage a mailbox can contain either mails or submailboxes, # but not both. Thunderbird separates these two by forcing server to # accept '/' suffix in mailbox names in subscriptions list. # The list is space-separated. #imap_client_workarounds = } ## ## POP3 specific settings ## protocol pop3 { # Login executable location. #login_executable = /usr/libexec/dovecot/pop3-login login_executable = /usr/libexec/dovecot/pop3-login=>加入# POP3 executable location. See IMAP's mail_executable above for examples # how this could be changed. #mail_executable = /usr/libexec/dovecot/pop3 # Don't try to set mails non-recent or seen with POP3 sessions. This is # mostly intended to reduce disk I/O. With maildir it doesn't move files # from new/ to cur/, with mbox it doesn't write Status-header. #pop3_no_flag_updates = no # Support LAST command which exists in old POP3 specs, but has been removed # from new ones. Some clients still wish to use this though. Enabling this # makes RSET command clear all Seen flags from messages. #pop3_enable_last = no # If mail has X-UIDL header, use it as the mail's UIDL. #pop3_reuse_xuidl = no # Keep the mailbox locked for the entire POP3 session. #pop3_lock_session = no # POP3 UIDL (unique mail identifier) format to use. You can use following # variables, along with the variable modifiers described in # <doc/wiki/Variables.txt> (e.g. %Uf for the filename in uppercase) # # %v - Mailbox's IMAP UIDVALIDITY # %u - Mail's IMAP UID # %m - MD5 sum of the mailbox headers in hex (mbox only) # %f - filename (maildir only) # # If you want UIDL compatibility with other POP3 servers, use: # UW's ipop3d : %08Xv%08Xu # Courier : %f or %v-%u (both might be used simultaneosly) # Cyrus (<= 2.1.3) : %u # Cyrus (>= 2.1.4) : %v.%u # Dovecot v0.99.x : %v.%u # tpop3d : %Mf # # Note that Outlook 2003 seems to have problems with %v.%u format which was # Dovecot's default, so if you're building a new server it would be a good # idea to change this. %08Xu%08Xv should be pretty fail-safe. # #pop3_uidl_format = %08Xu%08Xv # POP3 logout format string: # %i - total number of bytes read from client # %o - total number of bytes sent to client # %t - number of TOP commands # %p - number of bytes sent to client as a result of TOP command # %r - number of RETR commands # %b - number of bytes sent to client as a result of RETR command # %d - number of deleted messages # %m - number of messages (before deletion) # %s - mailbox size in bytes (before deletion) #pop3_logout_format = top=%t/%p, retr=%r/%b, del=%d/%m, size=%s # Maximum number of POP3 connections allowed for a user from each IP address. # NOTE: The username is compared case-sensitively. #mail_max_userip_connections = 3 # Support for dynamically loadable plugins. mail_plugins is a space separated # list of plugins to load. #mail_plugins = #mail_plugin_dir = /usr/lib/dovecot/pop3 # Workarounds for various client bugs: # outlook-no-nuls: # Outlook and Outlook Express hang if mails contain NUL characters. # This setting replaces them with 0x80 character. # oe-ns-eoh: # Outlook Express and Netscape Mail breaks if end of headers-line is # missing. This option simply sends it if it's missing. # The list is space-separated. #pop3_client_workarounds = } ## ## LDA specific settings ## protocol lda { # Address to use when sending rejection mails. postmaster_address = postmaster@example.com # Hostname to use in various parts of sent mails, eg. in Message-Id. # Default is the system's real hostname. #hostname = # Support for dynamically loadable plugins. mail_plugins is a space separated # list of plugins to load. #mail_plugins = #mail_plugin_dir = /usr/lib/dovecot/lda # If user is over quota, return with temporary failure instead of # bouncing the mail. #quota_full_tempfail = no # Format to use for logging mail deliveries. You can use variables: # %$ - Delivery status message (e.g. "saved to INBOX") # %m - Message-ID # %s - Subject # %f - From address #deliver_log_format = msgid=%m: %$ # Binary to use for sending mails. #sendmail_path = /usr/lib/sendmail # Subject: header to use for rejection mails. You can use the same variables # as for rejection_reason below. #rejection_subject = Automatically rejected mail # Human readable error message for rejection mails. You can use variables: # %n = CRLF, %r = reason, %s = original subject, %t = recipient #rejection_reason = Your message to <%t> was automatically rejected:%n%r # UNIX socket path to master authentication server to find users. #auth_socket_path = /var/run/dovecot/auth-master } ## ## Authentication processes ## # Executable location #auth_executable = /usr/libexec/dovecot/dovecot-auth # Set max. process size in megabytes. #auth_process_size = 256 # Authentication cache size in kilobytes. 0 means it's disabled. # Note that bsdauth, PAM and vpopmail require cache_key to be set for caching # to be used. #auth_cache_size = 0 # Time to live in seconds for cached data. After this many seconds the cached # record is no longer used, *except* if the main database lookup returns # internal failure. We also try to handle password changes automatically: If # user's previous authentication was successful, but this one wasn't, the # cache isn't used. For now this works only with plaintext authentication. #auth_cache_ttl = 3600 # TTL for negative hits (user not found). 0 disables caching them completely. #auth_cache_negative_ttl = 3600 # Space separated list of realms for SASL authentication mechanisms that need # them. You can leave it empty if you don't want to support multiple realms. # Many clients simply use the first one listed here, so keep the default realm # first. #auth_realms = # Default realm/domain to use if none was specified. This is used for both # SASL realms and appending @domain to username in plaintext logins. #auth_default_realm = # List of allowed characters in username. If the user-given username contains # a character not listed in here, the login automatically fails. This is just # an extra check to make sure user can't exploit any potential quote escaping # vulnerabilities with SQL/LDAP databases. If you want to allow all characters, # set this value to empty. #auth_username_chars = abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ01234567890.-_@ # Username character translations before it's looked up from databases. The # value contains series of from -> to characters. For example "#@/@" means # that '#' and '/' characters are translated to '@'. #auth_username_translation = # Username formatting before it's looked up from databases. You can use # the standard variables here, eg. %Lu would lowercase the username, %n would # drop away the domain if it was given, or "%n-AT-%d" would change the '@' into # "-AT-". This translation is done after auth_username_translation changes. #auth_username_format = # If you want to allow master users to log in by specifying the master # username within the normal username string (ie. not using SASL mechanism's # support for it), you can specify the separator character here. The format # is then <username><separator><master username>. UW-IMAP uses "*" as the # separator, so that could be a good choice. #auth_master_user_separator = # Username to use for users logging in with ANONYMOUS SASL mechanism #auth_anonymous_username = anonymous # More verbose logging. Useful for figuring out why authentication isn't # working. #auth_verbose = no # Even more verbose logging for debugging purposes. Shows for example SQL # queries. #auth_debug = no # In case of password mismatches, log the passwords and used scheme so the # problem can be debugged. Enabling this also enables auth_debug. #auth_debug_passwords = no # Maximum number of dovecot-auth worker processes. They're used to execute # blocking passdb and userdb queries (eg. MySQL and PAM). They're # automatically created and destroyed as needed. #auth_worker_max_count = 30 # Number of auth requests to handle before destroying the process. This may # be useful if PAM plugins leak memory. #auth_worker_max_request_count = 0 # Host name to use in GSSAPI principal names. The default is to use the # name returned by gethostname(). #auth_gssapi_hostname = # Kerberos keytab to use for the GSSAPI mechanism. Will use the system # default (usually /etc/krb5.keytab) if not specified. #auth_krb5_keytab = # Do NTLM authentication using Samba's winbind daemon and ntlm_auth helper. # <doc/wiki/Authentication/Mechanisms/Winbind.txt> #auth_ntlm_use_winbind = no # Path for Samba's ntlm_auth helper binary. #auth_winbind_helper_path = /usr/bin/ntlm_auth # Number of seconds to delay before replying to failed authentications. #auth_failure_delay = 2 auth default { # Space separated list of wanted authentication mechanisms: # plain login digest-md5 cram-md5 ntlm rpa apop anonymous gssapi otp skey # gss-spnego # NOTE: See also disable_plaintext_auth setting. mechanisms = plain # # Password database is used to verify user's password (and nothing more). # You can have multiple passdbs and userdbs. This is useful if you want to # allow both system users (/etc/passwd) and virtual users to login without # duplicating the system users into virtual database. # # <doc/wiki/PasswordDatabase.txt> # # By adding master=yes setting inside a passdb you make the passdb a list # of "master users", who can log in as anyone else. Unless you're using PAM, # you probably still want the destination user to be looked up from passdb # that it really exists. This can be done by adding pass=yes setting to the # master passdb. <doc/wiki/Authentication.MasterUsers.txt> # Users can be temporarily disabled by adding a passdb with deny=yes. # If the user is found from that database, authentication will fail. # The deny passdb should always be specified before others, so it gets # checked first. Here's an example: #passdb passwd-file { # File contains a list of usernames, one per line #args = /etc/dovecot.deny #deny = yes #} # PAM authentication. Preferred nowadays by most systems. # Note that PAM can only be used to verify if user's password is correct, # so it can't be used as userdb. If you don't want to use a separate user # database (passwd usually), you can use static userdb. # REMEMBER: You'll need /etc/pam.d/dovecot file created for PAM # authentication to actually work. <doc/wiki/PasswordDatabase.PAM.txt>#passdb pam {=>前面加入 ## [session=yes] [setcred=yes] [failure_show_msg=yes] # [cache_key=<key>] [<service name>] # # session=yes makes Dovecot open and immediately close PAM session. Some # PAM plugins need this to work, such as pam_mkhomedir. # # setcred=yes makes Dovecot establish PAM credentials if some PAM plugins # need that. They aren't ever deleted though, so this isn't enabled by # default. # # cache_key can be used to enable authentication caching for PAM # (auth_cache_size also needs to be set). It isn't enabled by default # because PAM modules can do all kinds of checks besides checking password, # such as checking IP address. Dovecot can't know about these checks # without some help. cache_key is simply a list of variables (see # <doc/wiki/Variables.txt>) which must match for the cached data to be used. # Here are some examples: # %u - Username must match. Probably sufficient for most uses. # %u%r - Username and remote IP address must match. # %u%s - Username and service (ie. IMAP, POP3) must match. # # The service name can contain variables, for example %Ls expands to # pop3 or imap. # # Some examples: # args = session=yes %Ls # args = cache_key=%u dovecot #args = dovecot#}=>前面加入 ## System users (NSS, /etc/passwd, or similiar) # In many systems nowadays this uses Name Service Switch, which is # configured in /etc/nsswitch.conf. <doc/wiki/AuthDatabase.Passwd.txt> #passdb passwd { # [blocking=yes] - See userdb passwd for explanation #args = #} # Shadow passwords for system users (NSS, /etc/shadow or similiar). # Deprecated by PAM nowadays. # <doc/wiki/PasswordDatabase.Shadow.txt>=>去除前面的 ##passdb shadow {# [blocking=yes] - See userdb passwd for explanation=>去除前面的 ##args ==>去除前面的 ##}# PAM-like authentication for OpenBSD. # <doc/wiki/PasswordDatabase.BSDAuth.txt> #passdb bsdauth { # [cache_key=<key>] - See cache_key in PAM for explanation. #args = #} # passwd-like file with specified location # <doc/wiki/AuthDatabase.PasswdFile.txt> #passdb passwd-file { # [scheme=<default password scheme>] [username_format=<format>] # <Path for passwd-file> #args = #} # checkpassword executable authentication # NOTE: You will probably want to use "userdb prefetch" with this. # <doc/wiki/PasswordDatabase.CheckPassword.txt> #passdb checkpassword { # Path for checkpassword binary #args = #} # SQL database <doc/wiki/AuthDatabase.SQL.txt> #passdb sql { # Path for SQL configuration file, see doc/dovecot-sql-example.conf #args = #} # LDAP database <doc/wiki/AuthDatabase.LDAP.txt> #passdb ldap { # Path for LDAP configuration file, see doc/dovecot-ldap-example.conf #args = #} # vpopmail authentication <doc/wiki/AuthDatabase.VPopMail.txt> #passdb vpopmail { # [cache_key=<key>] - See cache_key in PAM for explanation. # [quota_template=<template>] - %q expands to Maildir++ quota # (eg. quota_template=quota_rule=*:backend=%q) #args = #} # # User database specifies where mails are located and what user/group IDs # own them. For single-UID configuration use "static". # # <doc/wiki/UserDatabase.txt> # # "prefetch" user database means that the passdb already provided the # needed information and there's no need to do a separate userdb lookup. # This can be made to work with SQL and LDAP databases, see their example # configuration files for more information how to do it. # <doc/wiki/UserDatabase.Prefetch.txt> #userdb prefetch { #} # System users (NSS, /etc/passwd, or similiar). In many systems nowadays this # uses Name Service Switch, which is configured in /etc/nsswitch.conf. # <doc/wiki/AuthDatabase.Passwd.txt> userdb passwd { # [blocking=yes] - By default the lookups are done in the main dovecot-auth # process. This setting causes the lookups to be done in auth worker # proceses. Useful with remote NSS lookups that may block. # NOTE: Be sure to use this setting with nss_ldap or users might get # logged in as each others! #args = } # passwd-like file with specified location # <doc/wiki/AuthDatabase.PasswdFile.txt> #userdb passwd-file { # [username_format=<format>] <Path for passwd-file> #args = #} # static settings generated from template <doc/wiki/UserDatabase.Static.txt> #userdb static { # Template for the fields. Can return anything a userdb could normally # return. For example: # # args = uid=500 gid=500 home=/var/mail/%u # # If you use deliver, it needs to look up users only from the userdb. This # of course doesn't work with static because there is no list of users. # Normally static userdb handles this by doing a passdb lookup. This works # with most passdbs, with PAM being the most notable exception. If you do # the user verification another way, you can add allow_all_users=yes to # the args in which case the passdb lookup is skipped. # #args = #} # SQL database <doc/wiki/AuthDatabase.SQL.txt> #userdb sql { # Path for SQL configuration file, see doc/dovecot-sql-example.conf #args = #} # LDAP database <doc/wiki/AuthDatabase.LDAP.txt> #userdb ldap { # Path for LDAP configuration file, see doc/dovecot-ldap-example.conf #args = #} # vpopmail <doc/wiki/AuthDatabase.VPopMail.txt> #userdb vpopmail { #} # User to use for the process. This user needs access to only user and # password databases, nothing else. Only shadow and pam authentication # requires roots, so use something else if possible. Note that passwd # authentication with BSDs internally accesses shadow files, which also # requires roots. Note that this user is NOT used to access mails. # That user is specified by userdb above. user = root # Directory where to chroot the process. Most authentication backends don't # work if this is set, and there's no point chrooting if auth_user is root. # Note that valid_chroot_dirs isn't needed to use this setting. #chroot = # Number of authentication processes to create #count = 1 # Require a valid SSL client certificate or the authentication fails. #ssl_require_client_cert = no # Take the username from client's SSL certificate, using # X509_NAME_get_text_by_NID() which returns the subject's DN's # CommonName. #ssl_username_from_cert = no # It's possible to export the authentication interface to other programs: #socket listen { #master { # Master socket provides access to userdb information. It's typically # used to give Dovecot's local delivery agent access to userdb so it # can find mailbox locations. #path = /var/run/dovecot/auth-master #mode = 0600 # Default user/group is the one who started dovecot-auth (root) #user = #group = #} #client { # The client socket is generally safe to export to everyone. Typical use # is to export it to your SMTP server so it can do SMTP AUTH lookups # using it. #path = /var/run/dovecot/auth-client #mode = 0660 #} #} } # If you wish to use another authentication server than dovecot-auth, you can # use connect sockets. They are assumed to be already running, Dovecot's master # process only tries to connect to them. They don't need any other settings # than the path for the master socket, as the configuration is done elsewhere. # Note that the client sockets must exist in the login_dir. #auth external { # socket connect { # master { # path = /var/run/dovecot/auth-master # } # } #} ## ## Dictionary server settings ## # Dictionary can be used by some plugins to store key=value lists. # Currently this is only used by dict quota backend. The dictionary can be # used either directly or though a dictionary server. The following dict block # maps dictionary names to URIs when the server is used. These can then be # referenced using URIs in format "proxy::<name>". dict { #quota = mysql:/etc/dovecot-dict-quota.conf #expire = db:/var/lib/dovecot/expire.db } # Path to Berkeley DB's configuration file. See doc/dovecot-db-example.conf #dict_db_config = ## ## Plugin settings ## plugin { # Here you can give some extra environment variables to mail processes. # This is mostly meant for passing parameters to plugins. %variable # expansion is done for all values. # Quota plugin. Multiple backends are supported: # dirsize: Find and sum all the files found from mail directory. # Extremely SLOW with Maildir. It'll eat your CPU and disk I/O. # dict: Keep quota stored in dictionary (eg. SQL) # maildir: Maildir++ quota # fs: Read-only support for filesystem quota # # Quota limits are set using "quota_rule" parameters, either in here or in # userdb. It's also possible to give mailbox-specific limits, for example: # quota_rule = *:storage=1048576 # quota_rule2 = Trash:storage=102400 # User has now 1GB quota, but when saving to Trash mailbox the user gets # additional 100MB. # # Multiple quota roots are also possible, for example: # quota = dict:user::proxy::quota # quota2 = dict:domain:%d:proxy::quota_domain # quota_rule = *:storage=102400 # quota2_rule = *:storage=1048576 # Gives each user their own 100MB quota and one shared 1GB quota within # the domain. # # You can execute a given command when user exceeds a specified quota limit. # Each quota root has separate limits. Only the command for the first # exceeded limit is excecuted, so put the highest limit first. # Note that % needs to be escaped as %%, otherwise "% " expands to empty. # quota_warning = storage=95%% /usr/local/bin/quota-warning.sh 95 # quota_warning2 = storage=80%% /usr/local/bin/quota-warning.sh 80 #quota = maildir # ACL plugin. vfile backend reads ACLs from "dovecot-acl" file from maildir # directory. You can also optionally give a global ACL directory path where # ACLs are applied to all users' mailboxes. The global ACL directory contains # one file for each mailbox, eg. INBOX or sub.mailbox. cache_secs parameter # specifies how many seconds to wait between stat()ing dovecot-acl file # to see if it changed. #acl = vfile:/etc/dovecot-acls:cache_secs=300 # Convert plugin. If set, specifies the source storage path which is # converted to destination storage (mail_location) when the user logs in. # The existing mail directory is renamed to <dir>-converted. #convert_mail = mbox:%h/mail # Skip mailboxes which we can't open successfully instead of aborting. #convert_skip_broken_mailboxes = no # Skip directories beginning with '.' #convert_skip_dotdirs = no # If source storage has mailbox names with destination storage's hierarchy # separators, replace them with this character. #convert_alt_hierarchy_char = _ # Trash plugin. When saving a message would make user go over quota, this # plugin automatically deletes the oldest mails from configured mailboxes # until the message can be saved within quota limits. The configuration file # is a text file where each line is in format: <priority> <mailbox name> # Mails are first deleted in lowest -> highest priority number order #trash = /etc/dovecot-trash.conf # Expire plugin. Mails are expunged from mailboxes after being there the # configurable time. The first expiration date for each mailbox is stored in # a dictionary so it can be quickly determined which mailboxes contain # expired mails. The actual expunging is done in a nightly cronjob, which # you must set up: # dovecot --exec-mail ext /usr/libexec/dovecot/expire-tool #expire = Trash 7 Spam 30 #expire_dict = proxy::expire # Lazy expunge plugin. Currently works only with maildirs. When a user # expunges mails, the mails are moved to a mailbox in another namespace # (1st). When a mailbox is deleted, the mailbox is moved to another namespace # (2nd) as well. Also if the deleted mailbox had any expunged messages, # they're moved to a 3rd namespace. The mails won't be counted in quota, # and they're not deleted automatically (use a cronjob or something). #lazy_expunge = .EXPUNGED/ .DELETED/ .DELETED/.EXPUNGED/ # Events to log. Default is all. #mail_log_events = delete undelete expunge copy mailbox_delete mailbox_rename # Group events within a transaction to one line. #mail_log_group_events = # Available fields: uid, box, msgid, size, vsize # size and vsize are available only for expunge and copy events. #mail_log_fields = uid box msgid size }
啟動 dovecot
# vi /etc/inetd.conf找到...略...# Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3) server: pop3 stream tcp nowait root /usr/sbin/tcpd /usr/sbin/popa3d...略...改成...略...# Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3) server: #pop3 stream tcp nowait root /usr/sbin/tcpd /usr/sbin/popa3d pop3 stream tcp nowait root /usr/sbin/tcpd /usr/libexec/dovecot/pop3-login...略... # kill -HUP inetd(讓 inetd 重新讀取設定檔)
設定 Fail2ban
預防有人暴力測試 POP3的密碼,這裡預設讓使用者,使用收信軟體收信,
一般設定收信軟體時,會將帳號密碼設定進去,所以因該不會有密碼錯誤的問題發生
開啟 dovecot 的 log 檔(/var/log/pop3),發現有一些密碼錯誤的訊息:
dovecot: May 26 01:04:35 Info: auth(default): shadow(yahoo,111.222.333.444): Password mismatch
依據上列 log ,來產生 Fail2ban 使用的判斷式:
# cd /etc/fail2ban/filter.d
# vi dovecot-pop3imap.conf
[Definition]
failregex =Info: auth(default): shadow(.*,<HOST>): Password mismatch
# Option: ignoreregex# Notes.: regex to ignore. If this regex matches, the line is ignored.
# Values: TEXT
ignoreregex =加入 jail.conf 內
# vi /etc/jail.conf下列資料,加在到最後面## dovecot-pop3imap-tcpwrapper ## [dovecot-pop3imap] enabled = true filter = dovecot-pop3imap action = hostsdeny(當發現同一個來源IP有發生錯誤密碼,並且達十次, 會將該IP加入 /etc/hosts.deny 內)sendmail-whois[name=pop3, dest=abc@yahoo.com.tw](當有攔截到錯誤的密碼時,會發一封電子郵件通知您)logpath = /var/log/pop3 maxretry = 10 findtime = 1200 bantime = 1200 ## dovecot-pop3imap-iptables ## [dovecot-pop3imap] enabled = true filter = dovecot-pop3imap action = iptables-multiport[name=dovecot-pop3imap, port="pop3,imap", protocol=tcp](當發現同一個來源IP有發生錯誤密碼,並且達十次, 會將該IP加入 iptables 內,可使用 iptables -L 查看)sendmail-whois[name=pop3, dest=abc@yahoo.com.tw](當有攔截到錯誤的密碼時,會發一封電子郵件通知您)logpath = /var/log/pop3 maxretry = 10 findtime = 1200 bantime = 1200
其中 ## dovecot-pop3imap-iptables ##
及
## dovecot-pop3imap-tcpwrapper ##
可以都啟動,或是只選擇一個啟動。
重新讀取設定檔
# /etc/rc.d/rc.fail2ban reload